SEO 101
Nov 18, 2024
What is SEO?
SEO, or search engine optimization, is the technical process of ensuring a website meets the standards Google expects in order to rank in their algorithm. It increases the visibility of your website by appearing higher in organic search engine results.
Organic vs. Inorganic traffic
Organic traffic is driven by content and keywords on your site that most closely match a consumer’s search. It requires no ad spend and is strictly based on the experience your site provides. Inorganic traffic is traffic that is the result of paid advertising. This is when a company pays to have their site ranked as a top result for a specific keyword.
Organic traffic is important because it is a cost-free way for you to connect with your target audience and provide the unique experience that inorganic traffic cannot.
Why does it matter?
SEO is what allows your website and business to appear in the top rankings of these search results, driving consumers directly to your business.
- 93% of online interactions begin with a search engine
- 62% of consumers use search engines to learn about a new business, product, or service
- 41% of consumers use a search engine when they are ready to buy
What affects SEO?
There are a number factors that contribute to a site’s SEO score. This includes factors both on and off page:
- Quality and consistency of content publication
- Location details
- H1 Tags
- Metadata
- Keywords
- Image optimization
What can I do to start?
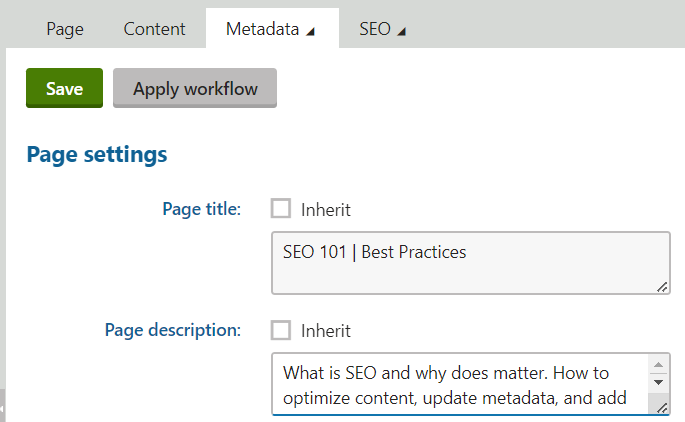
Update Metadata Titles and Descriptions
“Meta” tags are code tags that provide data about web pages but aren’t visible on the pages themselves.
The meta title tag tells search engines, web browsers, and social media websites what the title of a web page is. It is supposed to be an accurate description of the content found on the web page.
Most importantly, the meta title shows in your page’s listing in an online search result.
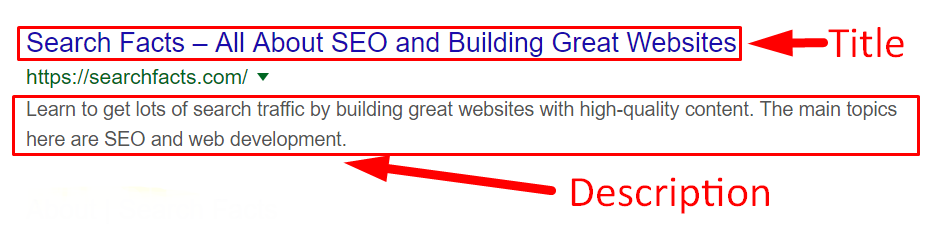
These can be managed for each individual page on your site under the Properties tab and under Metadata.
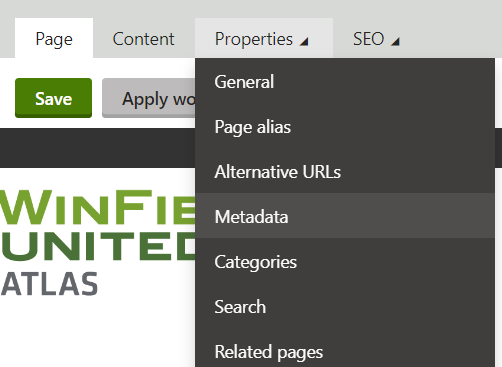
Title
- No more than 60 words
- Keywords that describe what's on the page
For example:
Your Agronomy page title might look like: Agronomy Services | Precision Agronomy | Crop Protection |
Description
- This is what shows in search results
- No more than 160 characters
- Long form description of the page
For example:
ABC Cooperative offers a full suite of agronomy services including crop consulting, precision agronomy technology, seed, nutrients, and crop protection.
Add H1 Heading Tags
Each page on your site should have one H1 tag. These are found in your actual page content, not in other header fields, and are established in site styling. Add an H1 (or Heading 1) to any page by checking the Enable H1 Header Tag box in a feature or hero widget. This will automatically set the Header Text for the widget as the H1 tag for that page.

You can also add an H1 by formatting text in a WYSIWYG widget using Headline 1 from the paragraph format drop down.
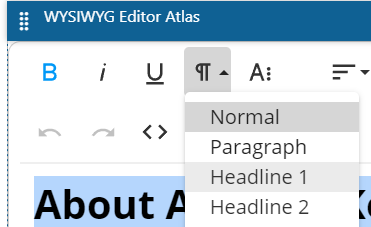
Be sure to only add one H1 tag per page! Contact the ATLAS support team for further assistance.
Page URLs
Each page’s URL should describe its content concisely.
Think about it this way:
If you had two page URLs:
/product/2789469760/
/adjuvants/ascend2/
Which one would you say is better optimized?
The second, of course, for the simple reason that it’s descriptive. By looking at the URL, you can identify that the page is about the Ascend2 product.
As a general rule of thumb, URLs should:
- Be descriptive and include the page’s primary keyword
- Use hyphens to separate words
- Use lowercase, rather than mixing in capital letters
- Be as short as possible while still describing the content of the page
User Experience
User experience (UX) refers to the overall interaction and satisfaction a person has while navigating your website.
UX influences SEO both directly and indirectly.
Poor UX can negatively impact your SEO, as it may cause visitors to spend less time on your site and leave quickly without taking meaningful actions. This signals to Google that your site might not deserve a high ranking in search results.
On the other hand, a positive UX indicates that your site is meeting users' needs, which can improve your rankings by making searchers more engaged.
Additionally, a strong UX can indirectly boost SEO by establishing your site as a valuable resource, encouraging others to link to it.
Develop Location Details Pages
Each of your locations should have a Location Details page with content specific to that location. These should include information such as hours, services offered at that location, and any other content specific to that location.
Interested in diving deeper into SEO? Contact the ATLAS team at atlas@landolakes.com to talk about our SEO audits and programs.
Images
Optimizing images enhances user experience and can improve your search rankings, especially in Google Images.
Check out our image optimization guide for practical tips to get started:
- Use descriptive file names
- Reduce file sizes and compress images to decrease loading times
- Write descriptive alt text to help search engines and improve accessibility
No SEO basics guide is complete without covering internal linking. Connecting pages within your site can:
- Help search engines grasp your site's structure
- Transfer authority (PageRank) between pages
- Encourage users to explore more of your content
Watch Getting Started with SEO support video
Closed captions available – click CC icon in videoWatch more support videos for ATLAS websites here >